Education | Intermediate history
Information
The people of Oman have been traders since ancient times. The first traders travelled overland in groups called caravans. They used camels and donkeys to carry their goods. The traders followed parts of the trails that linked China, India, Persia and Arabia with the Mediterranean countries. These routes have become known as the Silk Road.
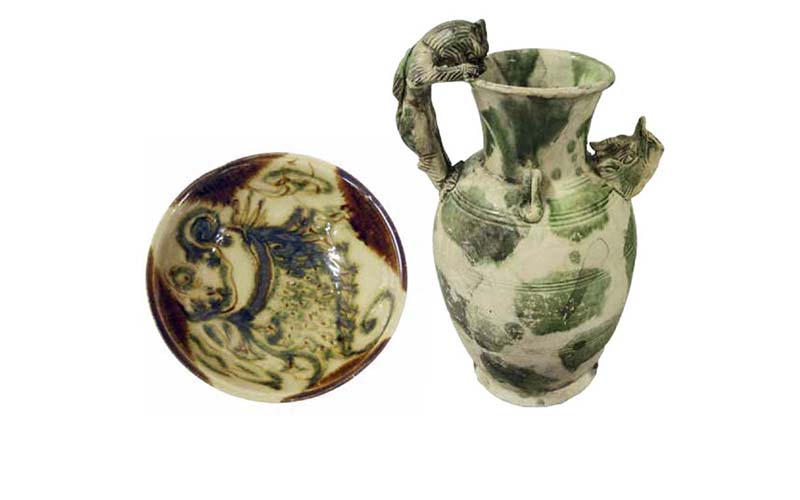
Many goods were traded along the Silk Road between different regions. From Arabia, traders carried dates, flax, cotton, vegetable dyes such as madder (red dye) and indigo (blue dye) and the aromatic resins frankincense and myrrh.
Goods brought back to Arabia from the East included spices such as pepper and star anise, silk, Chinese medicines and porcelains (pottery).

Traders expected to make great profits from selling their goods but the land routes were dangerous with deserts and mountain ranges to cross. A lookout had to be kept for bandits. Traders were often forced to pay for a safe passage as they entered new territories.
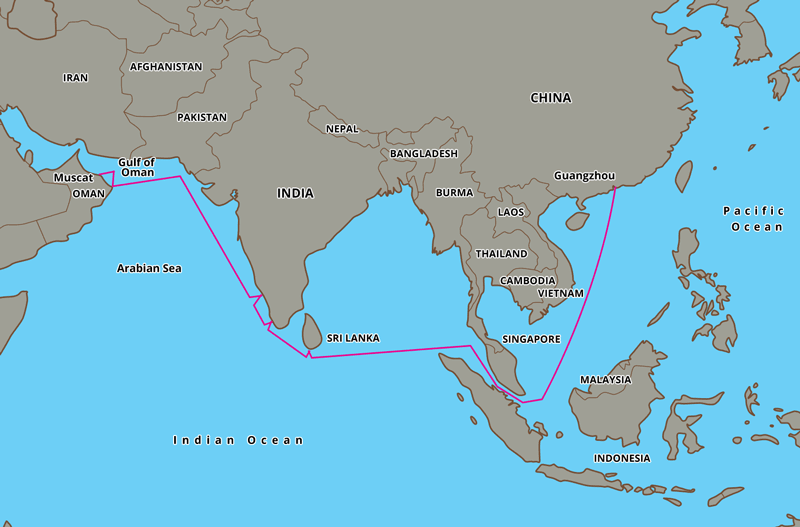
By the middle of the 9th century there was a trade route by sea between Muscat and China. Larger quantities of goods could be carried by ship but there were still many dangers. Desert sandstorms and bandits were replaced by storms at sea and pirates. And finding your way on the open ocean was far more difficult than following a trail on land.
While the main evidence of this trade comes from old documents, further proof came dramatically in 1998 with the discovery of an Arab trading vessel that was shipwrecked in the mid 9th century.
To understand more about these early trading voyages, a new ship, the Jewel of Muscat, was built. The ship is a reconstruction of the vessel discovered in 1998 and it sailed to Singapore following part of the ancient trade route to China.
Birth of Project
In this video, the Construction Director Tom Vosmer explains the importance of the shipwreck to the project. Information gained from the shipwreck about the hull, construction methods and materials will be used to reconstruct the 9th-century trading vessel, the Jewel of Muscat. The ship sailed to Singapore to be part of a museum.
01.21 mins
How do you sail a 9th-century trading ship?
During the voyage from Oman to Singapore the crew will live as the sailors did in the 9th century. However, the diet will be more varied and modern navigational equipment will be used to monitor the ship’s performance.
Research has revealed the following information about life on board an Arab trading ship during that period.
- Cooking: This was done over charcoal in a sand-filled wooden box open on one side.
- Food: The ship carried dates, dried and fresh fish, dried meat (camel and goat) and perhaps dried limes. Fresh food such as coffee, tea, bread, fruit and vegetables could be bought from ports along the way. The crew would have fished to add to their supplies.
- Water: The key to safe, long-distance voyaging was having a good supply of fresh water. Crews would collect water when it rained and take any opportunity to get water at ports along the way. Water was stored in wooden containers, goatskins and ceramic containers.
- Personal Hygiene: Washing was done in seawater. Toilets (or zoolies) were wooden boxes with a hole in the bottom and suspended over the side of the ship.
- Sleeping: It seems the crews on trading ships of this period generally slept on animal hides that were protecting the cargo.
- Navigation: Arab navigators were skilled observers of the world around them. They studied the sea, sky, currents and wave patterns and also looked for birds, whales and sea snakes that may give them a clue to where they were. Arab navigators used simple navigational equipment. A device called a kamal was used for determining the latitude and a weighted line was used for measuring the water depth as they approached land.
Test yourself
Answer the question or complete the sentence.
Test-summary
0 of 9 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
Information
Test yourself
Answer the question or complete the sentence.
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 9 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have answered 0 out of 0 questions correctly
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 9
1. Question
The Silk Road refers to trails between…
Correct
The Silk Road refers to trails between Arabia, India, Persia, China and Mediterranean Countries.
Incorrect
The Silk Road refers to trails between Arabia, India, Persia, China and Mediterranean Countries.
-
Question 2 of 9
2. Question
Which of the following was not imported into Arabia from the East?
Correct
Wheat was not imported into Arabia from the East.
Incorrect
Wheat was not imported into Arabia from the East.
-
Question 3 of 9
3. Question
The sea route from Arabia and China became possible when…
Correct
The sea route from Arabia and China became possible when ships were built that were capable of making long sea voyages.
Incorrect
The sea route from Arabia and China became possible when ships were built that were capable of making long sea voyages.
-
Question 4 of 9
4. Question
Which of the following was not taken on 9th-century voyages?
Correct
Yoghurt was not taken on 9th-century voyages.
Incorrect
Yoghurt was not taken on 9th-century voyages.
-
Question 5 of 9
5. Question
What is the best way to describe a zoolie?
Correct
A zoolie is a toilet.
Incorrect
A zoolie is a toilet.
-
Question 6 of 9
6. Question
In the 9th century sailors slept…
Correct
In the 9th century sailors slept on animal skins.
Incorrect
In the 9th century sailors slept on animal skins.
-
Question 7 of 9
7. Question
What did Arab navigators carefully observe to help find their way at sea?
Correct
Arab navigators carefully observed stars, the sun, the winds, wave patterns as well as birds and sea creatures.
Incorrect
Arab navigators carefully observed stars, the sun, the winds, wave patterns as well as birds and sea creatures.
-
Question 8 of 9
8. Question
What is a kamal?
Correct
A kamal is a navigational instrument.
Incorrect
A kamal is a navigational instrument.
-
Question 9 of 9
9. Question
On board a 9th-century trading vessel cooking was done…
Correct
On board a 9th-century trading vessel cooking was done in a sand-filled wooden box.
Incorrect
On board a 9th-century trading vessel cooking was done in a sand-filled wooden box.